Vaccines are challenging. They take time. The average time to bring a vaccine to market is 12 years. We still don’t have one for HIV/AIDS after 40 years. But for coronavirus, we are seeing estimates of just one year. It is not prudent to think that a vaccine is going to save the day.
This video outlines the challenges of vaccines. The vaccine may not work, it may be unsafe, and if it does work it may be too late to avert economic ruin.
Traditionally, vaccines have functioned by introducing the body to a version of the virus itself that doesn’t cause disease, or to an antigen that’s typically a protein on the virus surface. Both prime the immune system and spur it into action should someone encounter the virus. These two approaches provided the world with effective vaccines for polio, measles, hepatitis B, and other diseases.
But each time, researchers have to develop anew the biological machinery — cells and reactor conditions — needed to manufacture the vaccines.
TECHNOLOGIES
FasterCures, a center of the Milken Institute, is currently tracking the development of treatments and vaccines for COVID-19 (coronavirus). This tracker contains an aggregation of publicly-available information from validated sources.
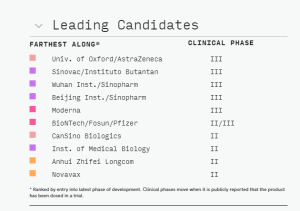 According to Milken, there are 212 Vaccines in development in 9 categories. 34 of which are now in testing.
According to Milken, there are 212 Vaccines in development in 9 categories. 34 of which are now in testing.
The leading vaccine candidates as of mid September 2020 are listed here.
Twelve to eighteen months is considered a short time to develop a vaccine. They are now thinking in record time, but development will be with limited safety testing.
- Inovio Pharmaceuticals: Inovio Pharmaceuticals primarily develops DNA-based medicines and was founded in 1979. Inovio reported their new COVID-19 vaccine in development, INO-4800, in January 2020, and has since begun Phase I trials. Inovio claims they will be able to produce one million INO-4800 vaccines by the end of the year, but the practicality of this claim has yet to be proven. Inovio stocks (NASDAQ: INO) have increased from $3.69 to $24.15 in the past six months, an increase of 552.85%. It should be noted that as of June 24, 2020, Inovio stocks have risen from $15.30 to $24.15 in the past two days. Inovio’s market cap has increased from $334.49 M to $2.42 B since December 31st, 2019 (Stock Price as of Sept 8th. $10.07).
x - Moderna: Moderna specializes in mRNA-based drug discovery and development and was founded in 2010. Moderna began developing their vaccine, mRNA-1273, around the same time as Inovio’s DNA-based INO-4800, both of which are currently undergoing human trials 51. Moderna stocks (NASDAQ: MRNA) have increased from $19.75 to $63.84 in the past six months, an increase of 223.24%. Moderna’s market cap has increased from $6.58 B to $24.63 B since December 31st, 2019 (Stock Price as of Sept 8th. $55.65).
x - Novavax: Novavax is a biotechnology company which specializes in vaccine development. Novavax already had a new flu vaccine under development prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, and has since announced their candidate vaccine, NVXCoV2373, which began human trials in May 2020. Novavax stocks (NASDAQ: NVAX) have increased from $4.00 to $76.81 in the past six months, an increase of 1820.25%. Likewise, Novavax’s market cap has increased from $128.76 M to $3.80 B since December 31st, 2019 (Stock Price as of Sept 8th. $91.86).
RESOURCES
In March 2020, the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) initiated an international COVID-19 vaccine development fund, with the goal of raising US$2 billion for vaccine research and development, and committed to investments of US$100 million in vaccine development across several countries.
Also in March, the Canadian government announced CA$275 million in funding for 96 research projects on medical countermeasures against COVID-19, including numerous vaccine candidates at Canadian universities, with plans to establish a “vaccine bank” of new vaccines for implementation if another coronavirus outbreak should occur.
