OUTPATIENT (HOME) THERAPY
A paper authored by 23 physicians (currently in pre-print) outlines key pathophysiological principles that relate to the patient with early infection treated at home. Their conclusion is that it is conceivable that some if not a majority of hospitalizations could be avoided with a treat-at-home first approach with appropriate telemedicine monitoring and access to oxygen and therapeutics.
An algorithm based on age and comorbidities that allows for a large proportion to be monitored and treated at home during self-isolation with the aim of reducing the risks of hospitalization and death.
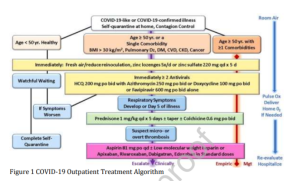
Therapeutic approaches based on these principles:
- reduction of re-inoculation
- combination antiviral therapy
- immunomodulation
- antiplatelet/antithrombotic therapy
- administration of oxygen, monitoring, and telemedicine
The paper discusses the following:
- Control of Contagion
- Reduction of Self-Re-inoculation
- Combination Antiviral Therapy
- Zinc Lozenges and Zinc Sulfate
- Antimalarials
- Azithromycin
- Doxycycline
- Favipiravir
- Immunomodulators
- Colchicine
- Antiplatelet Agents and Antithrombotics
- Delivery of Oxygen and Monitoring
